What is a cloud audit?
A cloud audit is a periodic examination an organization does to assess and document its cloud vendor’s performance. The goal of such an audit is to see how well a cloud vendor is doing in meeting a set of established controls and best practices.
The Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) provides audit documents, guidance and controls that an IT organization can use to examine its cloud vendors. Third-party auditors can also use CSA audit materials. CSA resources are considered the primary audit tools to perform and optimize a comprehensive cloud audit.
The term CloudAudit refers to a specification the CSA developed in 2019 for the presentation of information about how a cloud service provider addresses control frameworks. The goal of CloudAudit was to provide cloud service providers with a way to make their performance and security data readily available for potential customers.
[embedded content]
How do you conduct a cloud audit?
An audit of a cloud environment is similar to an IT audit. Both examine a variety of operational, administrative, security and performance controls. Cloud audit controls are also similar to IT audit controls but with a focus on the nuances of cloud environments.
Cloud vendors offer several on-demand, as-a-service resources, such as software as a service and platform as a service. Audits help assure these offerings are delivered with the appropriate attention to specific controls, especially those involving security policies and risk management. Audits of cloud computing services look for evidence that a cloud vendor is using best practices, complies with appropriate standards and meets certain benchmarks in delivering its services.
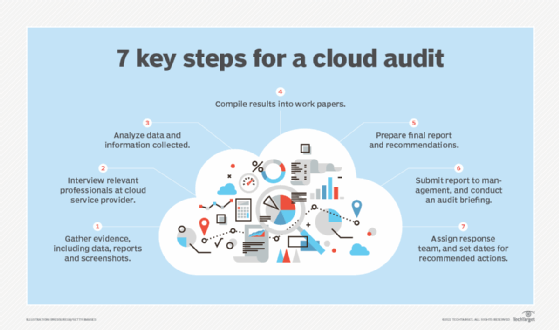
When performing a cloud audit, take the following basic steps:
- Gather evidence. Collect relevant documents and other evidence, such as screenshots.
- Interview. Ask cloud vendor personnel how the provider operates and delivers its services. CSA has cloud audit questions and checklists that can be useful to both external and internal auditors. CSA has partnered with ISACA to define what constitutes relevant cloud audit knowledge and provide accreditation resources for cloud audit professionals.
- Analyze. Look at how well the vendor’s processes align with CSA and ISACA controls.
- Compile results. Combine analysis with the evidence from documentation and interviews into work papers that are used to prepare a final report and recommendations.
- Prepare final report. Submit it to the organization’s management, usually during a formal audit briefing.
- Take action. Management sets dates for responses to the recommended actions and assigns a team to respond to the audit report.
Cloud audit tools
CSA provides tools and guidance auditors need to perform a cloud audit. The table below lists these items and their availability.
| Resource | Description | Link |
| Cloud Controls Matrix (CCM) v4 | Cybersecurity control framework for cloud computing aligned to CSA best practices | CCM and Consensus Assessment Initiative Questionnaire (CAIQ) v4 (downloadable document) |
| Security, Trust, Assurance and Risk (STAR) security questionnaire | Checklist tool to ask cloud vendors about security controls | STAR Level 1 Security Questionnaire (downloadable document) |
| STAR Registry | List of cloud vendors’ security and regulatory compliance postures | STAR Registry listing |
| CSA best practices | Guidance on cloud security, performance and auditing | CSA Security Guidance (downloadable document) |
| Mapping to other standards | Mapping CCM v4 to other industry standards, such as the International Organization for Standardization 27000 series and Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard | Included in CCM and CAIQ v4 |
| Controls Applicability Matrix | Help for auditors to decide the most appropriate controls to use for a specific vendor | Included in CCM and CAIQ v4 |
| CCM Metrics | Compendium of security metrics for clouds to support governance, risk and compliance activities | Included in CCM and CAIQ v4 |
| CCM v4 Implementation Guidelines | Guidelines for using the CCM v4 audit standards | Included in CCM and CAIQ |
| Continuous Audit Metrics Catalog | Guidance to plan and implement continuous cloud audit activities | Continuous Audit Metrics (downloadable document) |
| CCM v4 Auditing Guidelines | Guidance for planning, organizing and conducting a cloud audit engagement using CCM v4 | Available Q4 2021 |
Cloud audit professional credentials
The CSA and ISACA jointly offer the following cloud audit credentials:
- Certificate of Cloud Security Knowledge is a body of knowledge in cloud technology areas, including cloud processing and security. It is a first step in preparation for the companion certification in cloud auditing knowledge.
- Certificate of Cloud Auditing Knowledge trains candidates in how to audit cloud platforms and security.
Both certificates complement ISACA credentials. They provide evidence of an auditor’s knowledge of cloud infrastructure and systems, security and vulnerabilities, and they show that the auditor knows how to conduct a cloud audit.
Find out what to include in a cloud audit checklist to optimize your organization’s cloud compliance strategy.
This was last updated in November 2021
Continue Reading About cloud audit

