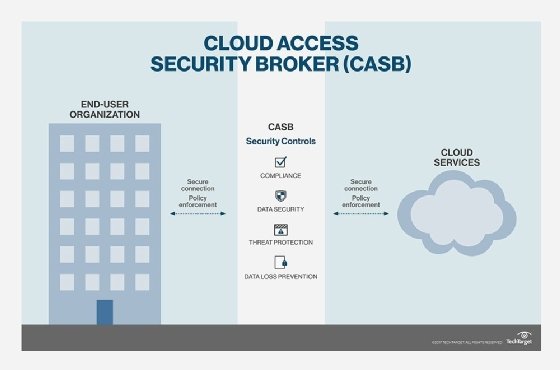
A cloud access security broker (CASB) is a software tool or service that sits between an organization’s on-premises infrastructure and a cloud provider’s infrastructure. CASBs are available as both an on-premises or cloud-based software as well as a service.
Four pillars of CASB
A CASB acts as a gatekeeper, allowing organizations to extend the reach of their security policies beyond their own infrastructure.
CASBs typically offer the following:
- Firewalls to identify malware and prevent it from entering the enterprise network
- Authentication to check users’ credentials and ensure they only access appropriate company resources
- Web application firewalls (WAFs) to thwart malware designed to breach security at the application level, rather than at the network level
- Data loss prevention (DLP) to ensure that users cannot transmit sensitive information outside of the corporation
How does a CASB work?
CASBs work by ensuring that network traffic between on-premises devices and the cloud provider complies with an organization’s security policies.
The value of cloud access security brokers stems from their ability to give insight into cloud application use across cloud platforms and identify unsanctioned use. This is especially important in regulated industries.
CASBs use autodiscovery to identify cloud applications in use and identify high-risk applications, high-risk users and other key risk factors. Cloud access security brokers may enforce a number of different security access controls, including encryption and device profiling. They may also provide other services such as credential mapping when single sign-on is not available.
This article is part of
Use cases for CASBs
CASB tools have evolved to include, or work alongside, other IT security services — though some vendors, such as Netskope and Bitglass, still offer standalone tools. CASBs are particularly useful in organizations with shadow IT operations or liberal security policies that allow operating units to procure and manage their own cloud resources. The data CASBs collect can be used for reasons other than security, such as monitoring cloud service usage for budgeting purposes.
Vendors and resources
Vendors in the cloud access security space include Skyhigh Networks, CipherCloud, McAfee and Symantec. Microsoft includes CASB functionality in its base Azure security services at no extra charge. To meet the needs of IaaS and PaaS users, CASB vendors have added or expanded functionality for security tasks, such as the following:
- Single sign-on (SSO). Allows an employee to enter their credentials one time and access a number of applications.
- Encryption. Encrypts information from the moment it’s created until it’s sitting at rest in the cloud.
- Compliance reporting tools. Ensure that the company’s security systems comply with corporate policies and government regulations.
- User behavior analytics. Identifies aberrant behavior indicative of an attack or data breach.
[embedded content]
This was last updated in January 2021
Continue Reading About cloud access security broker (CASB)
