“Each line of business is driving digital transformation in its own way,” says Naveen Kamat, executive director and CTO of data and AI services at Kyndryl, an IT infrastructure services provider. “They are setting up their own apps in the cloud, which generate data daily. Then there’s web and social media data coming in. The enterprise data estate is becoming much, much bigger; it’s becoming much more complex to manage.”
The insurance industry provides an example of today’s data landscape complexity. One substantial challenge to good data management in insurance is a plethora of legacy systems built up over the years, says Ali Shahkarami, chief data officer at Allianz Global Corporate & Specialty (AGCS). “That’s especially true for international companies operating across borders with different products, regulatory requirements, and reporting requirements,” he notes. “The ability to do that centrally and in a consistent manner is a big challenge. It impacts everything you build with data and analytics.”
Unfortunately, while data management has become more challenging, data management skills have become harder to come by. The number of skilled data personnel has stayed the same or even dropped over the last decade, even as the number of data and application silos have increased, says Gartner. That means it takes more time than ever to meet integrated data analytics needs.
The consequences for organizations that fail to manage their data effectively and efficiently are becoming dire. For one thing, the cost of inadequate data management is growing. The cost of poor data can be about 20% of revenue, estimated Thomas C. Redman, president of consultancy Data Quality Solutions, in a co-authored MIT Sloan Management Review article.
“Almost all work is plagued by bad data,” write Redman and Thomas H. Davenport. “The salesperson who corrects errors in data received from marketing, the data scientist who spends 80% of his or her time wrangling data, the finance team that spends three-quarters of its time reconciling reports, the decision maker who doesn’t believe the numbers and instructs his or her staff to validate them.”

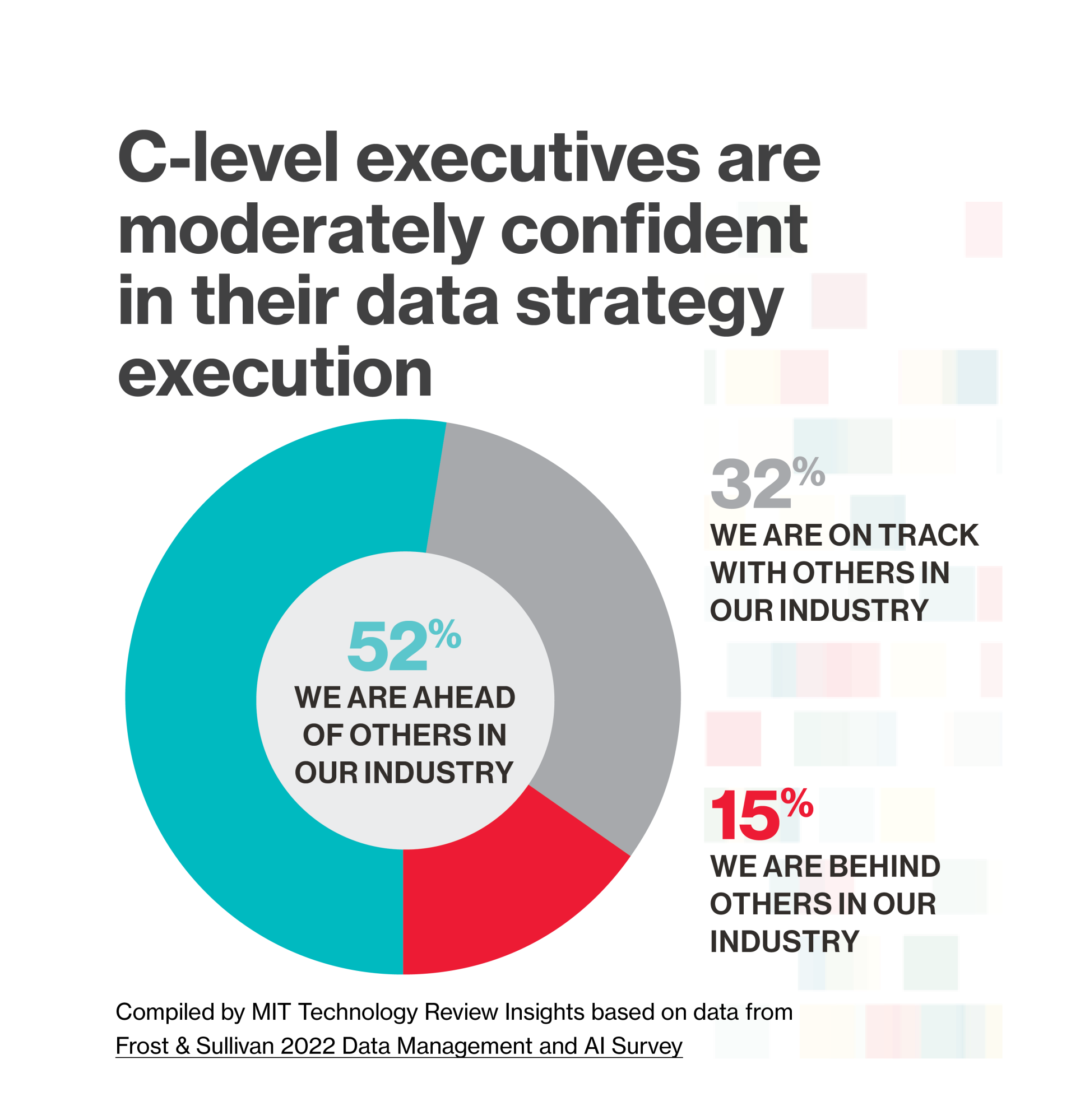
Redman and Davenport estimate that less than 5% of companies use their data and data science to gain a competitive edge. “Companies are not seizing the strategic potential in their data,” they conclude.
When it comes to implementing advanced technologies, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, inadequate data management represents a substantial barrier. Not only could AI programs be ineffective, but “without the right data, building AI is risky and possibly dangerous” if data bias, diversity, and systematic labeling are not part of a data management strategy, says Rita Sallam, distinguished vice president and analyst at Gartner.
This content was produced by Insights, the custom content arm of MIT Technology Review. It was not written by MIT Technology Review’s editorial staff.
